
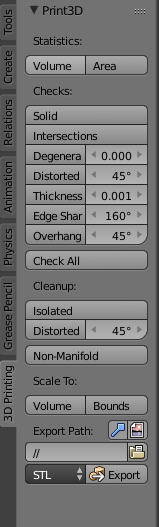
In the case of the cube where all sides are 2 meters, this reads as 2x2x2=8, so the volume is 8 meters cubed. While area takes the height and depth of each face and adds all the faces together, the volume is the height * width * length of the object. Volume on the other hand is the area that the object itself takes up. So 2×2=4 and then 4×6=24, meaning that the area is 24 meters squared. For example, a cube has 6 sides, and every side is 2×2 meters in size. The area of a 3D object is the surface area of all of the objects’ faces combined. There are numerous potential limitations that can hinder the creation of a good 3D model, so below we have a list of what limitations the 3D print toolbox can help identify: Volume And Areaįirst, you have the ability to calculate the volume and area of an object, as these are important for defining the size of your model when printing. This allows you to actually identify where the problem geometry is on the model.Ī Breakdown Of What You Can Do With The 3D Print Toolbox The same applies to any other options in the list, such as selecting non-flat faces. If for example, the nonmanifold edge becomes available, then you can click the button and all edges that are classed as nonmanifold edges become selected on the model. Then we transition from object mode to edit mode, and when you do you may find that some of the options transform into buttons if the value is greater than 0. Remember that there are parameters that your printer will be able to work within, so there might be a tiny bit of leeway.
BLENDER 3D PRINTING TOOLBOX SOFTWARE
When you send your model to the software used to create the actual 3D print, the model will need to be suitable for 3D printing but does not need to be perfect. If you are using your own 3D printer at home or in your business, then we recommend researching the limitations of your selected printer, and possibly creating some dummy models to test first. The idea of the 3D print toolbox is so that you can control the threshold at which faces will be deemed no longer usable, as there is no definitive value, this falls on the hardware that you are using. It is unlikely that your 3D model will ever be truly perfect, especially if you are adding more detail, like with sculpting for example. Is it Ok If My Model Is Not Perfect For 3D Printing? As you can tell, messing up a printed model can be costly, both in terms of time and money. Getting a model wrong for a video game simply means importing the model back to Blender, and editing it so that any errors are corrected, before sending it back to the game engine.īy contrast, a 3D printed model requires a significant amount of time to create, as well as cost for the materials used for printing. It is very easy to design a model for virtual purposes, but much harder for creating actual physical products. An example of such a limitation is the size of the model, as each 3D printer is capable of producing objects in a certain size range. 3D printers are limited in their capabilities and so as the designer of the object you need to ensure that the model falls within these limitations. The 3D print toolbox is designed primarily to identify geometry that is likely to cause issues with the printing process. What Is The 3D Print Toolbox Actually Designed To Do? This is perhaps the single most important add-on that you can use for 3D printing in Blender, but what exactly does it do and how can it help to construct printable 3D objects? To locate the toolbox, press the N key on the viewport to open the side panel, and select the print toolbox tab. To activate the Print Toolbox Addon, first, go to Edit > Preferences > Add Ons, and in the search bar in the top corner type in print toolbox, making sure the tickbox is enabled before closing the preferences panel. To make life easier, Blender has an add-on for helping to construct models for the purpose of 3D printing.
Blender is capable of creating 3D printable objects and then sending them to an application used for the 3D printing process. One of the fastest-growing industry subsets today is the field of 3D printing, the ability to design an object virtually and then construct that object as a single piece using specialized tools and software.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
